
Remediation of Heavily Contaminated Soils and Sediments: Chelator Combination, Recovery, and Media Effect
Zhanna Katz, Environmental Engineering, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, israel
Amos Ullmann, Environmental Engineering, Tel-aviv University, Tel-aviv, Israel
Neima Brauner, Environmental Engineering, Tel-aviv University, Tel-aviv, Israel
Zvi Ludmer, Biochemistry, Hebrew University, Rehovot, Israel
Roman Goikhman, Biochemistry, Hebrew University, Rehovot, Israel
Contamination of soils and sediments by heavy metals is a worldwide-recognized problem. Methods of soil/sediments analysis and remediation usually involve use of chelators. Strong and highly efficient chelators are mostly non-biodergadable, whereas environmentally-friendly chelators are often not powerful enough towards heavy metal extraction from highly contaminated media.
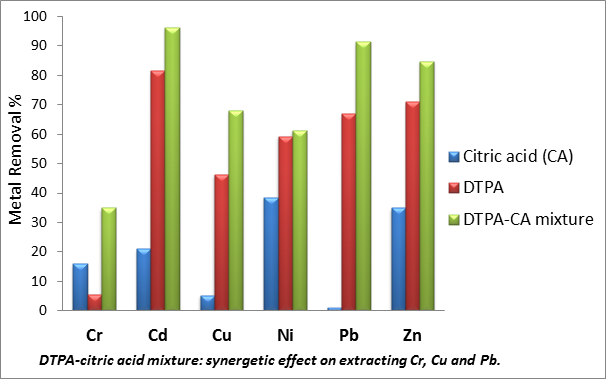
We have developed a process that allows extracting most of hazardous metals from soils, sediments and sludge, using chelator combination of citric acid and EDDS (or DTPA). We have observed some synergetic effect with a chelator pair, and solvent effect (organic vs aqueous solution). Remediation of soil/sludge and sediments is compared and discussed. Due to large amounts of the chelators needed for efficient soil remediation, chelator recovery-reuse approach was investigated and optimized. We believe that the present research could contribute to the art of soil remediation.
Organized & Produced by:

POB 4043, Ness Ziona 70400, Israel
Tel.: +972-8-9313070, Fax: +972-8-9313071
Site: www.bioforum.co.il,
E-mail: bioforum@bioforum.co.il